What is hydropower and how does it work?
renewable energy

renewable energy
With the global call to action to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, hydropower is becoming an increasingly important energy source. As one of the most consistent and reliable renewable energy sources, hydro projects will continue long into the future.
Hydropower is one of the cheapest ways to generate electricity and is used by more than 60 countries worldwide, meeting half of their electricity demand. It also provides the added benefits of being a clean energy source, providing energy ‘on demand’ and creating thousands of jobs across the globe.
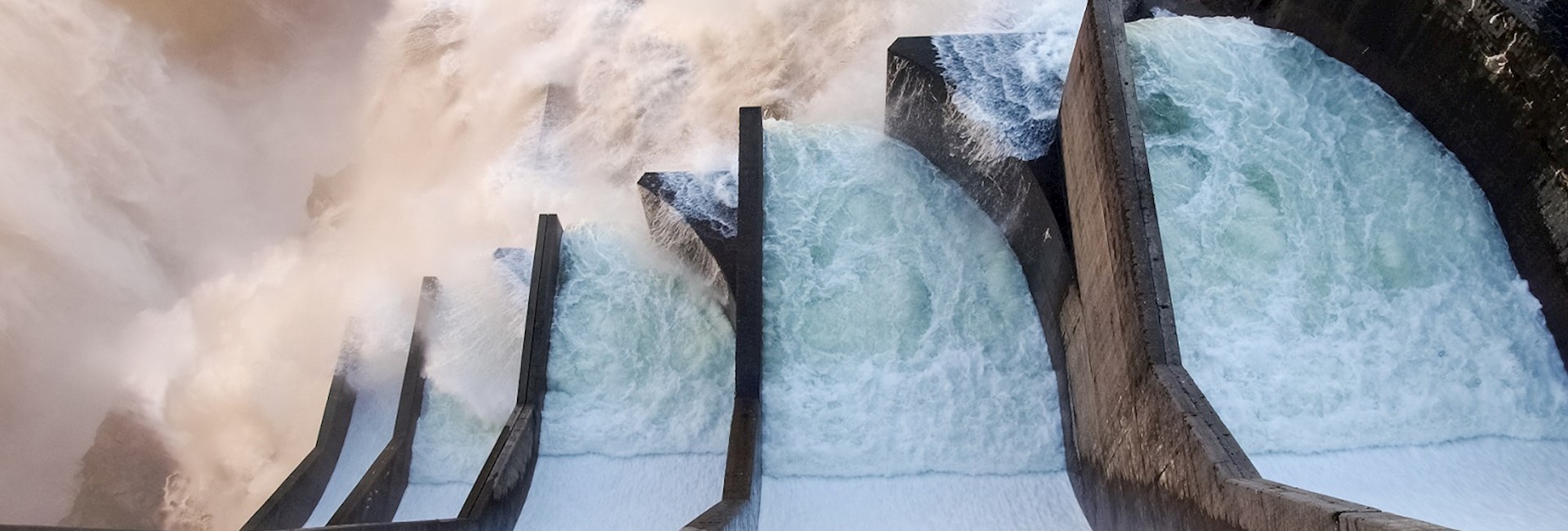
Hydropower is energy generated from water sources like the ocean, waterfalls and rivers. Because water constantly moves through a global cycle, it’s movement can be harnessed to generate electricity or to drive machinery. Because water is an infinite resource, its cycle provides an endless recharging system, making it a renewable energy source.
There are several types of hydropower facilities and they’re all powered by the movement of flowing water. Turbines and generators are used to convert the water’s kinetic energy into electricity, which is then fed into the electric grid to supply homes, businesses and industries.
A new technology called microhydro is increasingly being used in remote areas to power homes and businesses. The technology makes it possible for small holdings to generate their own energy, independent from large hydropower plants. Microhydro uses smaller water flows to run small generators that produce enough energy to power a home, or run on-site equipment.

Hydropower works by harnessing the energy that comes from the flow of water through a turbine connected to a generator, thus turning it into electricity. Most hydropower plants store water in a dam, which is controlled by a gate or valve to measure the amount of water that flows out. The greater the elevation of the dam, the more energy can be generated.
Just before the water flows over the dam, it gains potential energy, which is converted into kinetic energy as it flows downhill. The water is used to turn a turbine, which is connected to an electric generator that distributes the power to the end users.
There are four main types of hydropower facilities:

Hydropower is used to provide homes and businesses with electricity. It’s also used to power machinery. Traditionally, hydropower was used to drive mills to grind grain.
Nowadays, with the right terrain and financing, hydropower systems can be set up to generate electricity for homes and businesses in rural locations. Homeowners and businesses can also make use of government tariffs and agreements and sell the energy they don’t use back to the grid.
As well as generating energy, the reservoirs created at hydropower plants provide recreational opportunities like boating, swimming and fishing. They can also be used to provide water supply, flood control and irrigation.
Hydropower is a renewable energy because it uses the earth’s natural water cycle to generate electricity. No direct emissions are released into the atmosphere during the process, so it’s considered a clean form of energy generation.
However, no process that disrupts the natural balance of ecosystems is without its negative impact. For example, some consider the large volumes of water stored in hydropower plants controversial due to the global water shortage.
Hydropower can also block the migration of fish to their spawning grounds. This often results in the decline of the number of fish in rivers and in some cases, can cause extinction of species.
There’s also the argument that vegetation gets trapped in reservoirs and releases carbon dioxide and methane, which contributes to global warming.
Hydropower offers many benefits to households, businesses and the environment. For one, it’s a very predictable and consistent source of energy. The water on our planet will never run out, and so hydropower is a sustainable and green energy source.
As such, hydropower is well-suited to meeting peak energy demand and is more responsive than many other renewable energy sources. Hydropower plants can adjust the flow of water, which allows the plant to produce more energy when required and reduce it when it’s not needed.
Hydropower generators are also more reliable than other forms of electricity generation. For example, a generator can have a lifespan of up to 100 years and requires little maintenance over its lifetime.
The creation of hydropower sites can also benefit nearby towns. Jobs are created at the plant itself, and because dams can only be built in rural locations, skilled workers are needed to build roads, mange transport and build equipment. This can also open up new paths for rural areas and provide additional infrastructure.
Hydropower also works well in combination with other renewable sources. Because hydro is consistent and reliable, it can be used to supplement solar and wind power, both of which can be more intermittent in their supplies of energy.
Despite all the benefits of hydropower, it does have its downsides. The most obvious being, that hydropower plants can only be built on very specific locations, i.e., next to a water supply or in a rural location.
Likewise, the costs of developing a hydropower plant can be very high. Large-scale projects in particular require significant investment, and there can be other conditions attached to their development, which add to the overall capital.
Although impoundment and tidal power are very reliable energy sources, run-of-the-river systems require a constant flow of water. As such, river-run hydro is dependent on the weather as it requires rainfall to create enough flow to turn a turbine. With this is mind, river-run hydro can be susceptible to drought. As climate change continues to raise the temperature of the planet, this problem could become more common in the near future.
At the other end of the scale, impounding hydro can present a flood risk. Because dams are built on high elevations, they pose a risk to any nearby towns. Although dams are built to be very strong, they can still burst and cause devastation to the surrounding landscape. The biggest dam failure in history was in 1975, when the Banqiao Dam in China burst due to excess rainfall from a typhoon and killed 170,000 people.
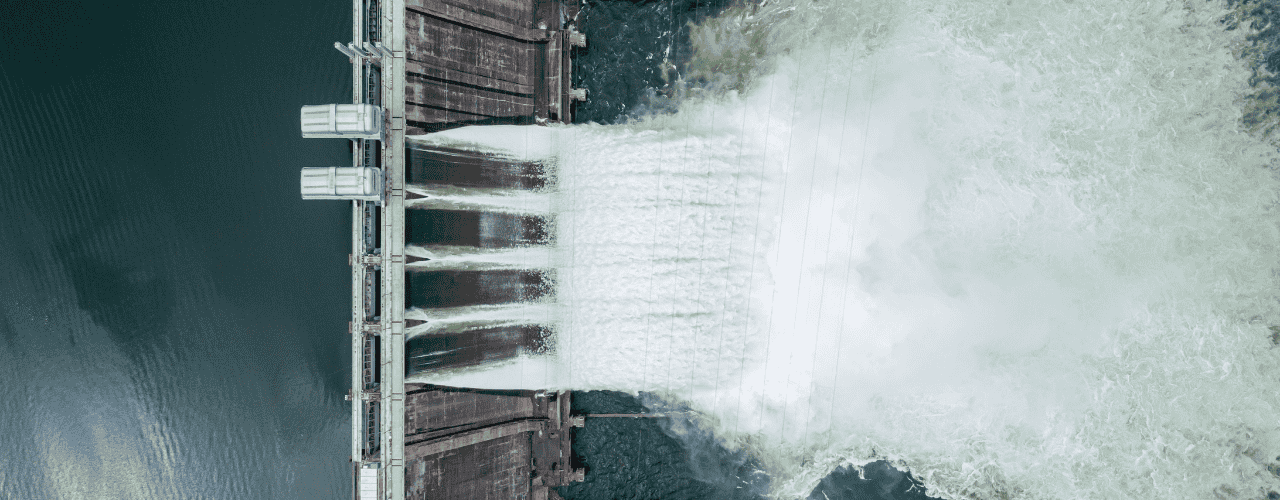
The impact that a hydropower project has on the environment depends on its size. A small-scale run-of-the-river project will have less of an impact than a larger impoundment project.
There are other variables that can impact hydropower projects like the type of technology being used and how much additional infrastructure is required in the surrounding area.
Of course, every hydropower project requires careful planning and adherence to best practices and compliance. Although the development of hydro sites does require some disruption to the environment, the process is carefully monitored.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), 17% of the world’s electricity is supplied by hydropower. It is the most widely-used renewable energy source in the world.
The Energy Information Administration confirms that China is the largest producer of hydropower, followed by Canada, Brazil and the United States.

According to the 2020 Hydropower Status Report, total global hydropower installed capacity reached 1,308 gigawatts (GW) in 2019, as 50 countries and territories completed greenfield and upgrade projects.
With the world investing more into reducing our dependence on fossil fuels, there has never been a better time to work in hydropower. There’s a lot of research and development happening in the field today, and new technologies are helping meet the energy needs of businesses and people every day.
If you want to combine an interesting and challenging career with helping protect the planet’s future, then working in hydropower could be the career for you.
If you’re looking for a job in hydropower, Brunel should be your first call. We have many jobs in the renewable energy sector. We help companies staff their projects in nearly 40 countries across dozens of specialisms.
With a 45-year track record, we recruit for hundreds of the most inspiring companies across the globe.
As recruitment specialists to the renewable energy sector, we bring together challenging projects and ambitious talent. If you’re ready to take the next step in your career, check out the opportunities on our renewable energy job listings.
Wuppertal
40 hrs a week
22 December 2026
Wuppertal
40 hrs a week
22 December 2026
Wuppertal
40 hrs a week
22 December 2026
Wuppertal
40 hrs a week
22 December 2026
Are you looking for a career change or just starting out in the job market? Whether you are interested in sectors such as Life Sciences, Mining, Renewables or Conventional Energy, you will find a broad variety of fascinating career opportunities.